Technology
The Dark Web: Exploring the Hidden Layers of the Internet
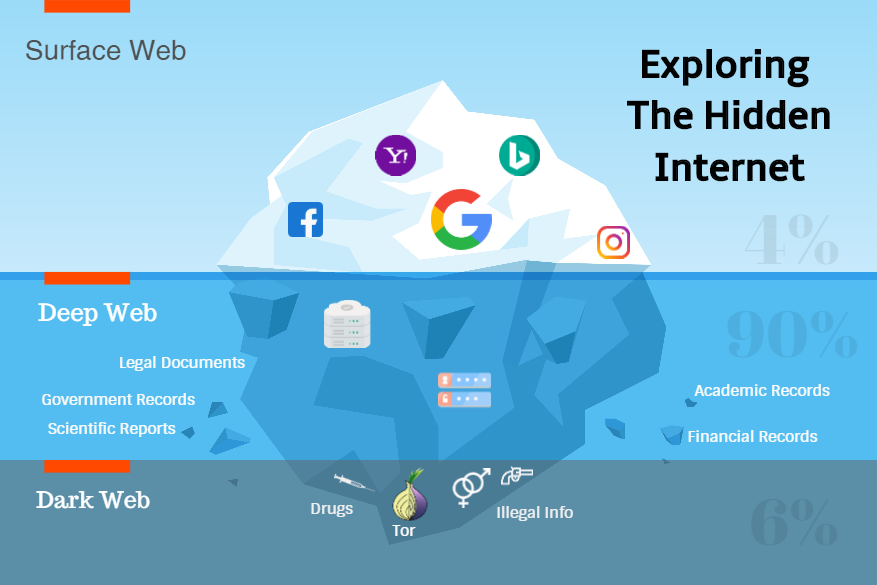
The internet, as most of us know it, is a vast ocean of information readily accessible through search engines like Google or Bing. But beneath the surface lies a hidden realm known as the dark web. This shrouded corner of the internet, often conjuring images of illegal activity and criminal marketplaces, is a complex and misunderstood concept. This comprehensive exploration delves into the dark web, examining its origins, the technology that facilitates it, its potential dangers, and its surprising legitimate uses.
1. Demystifying the Deep Web vs. Dark Web
It’s crucial to distinguish between the deep web and the dark web:
- Deep Web: This encompasses all content not indexed by search engines. It includes private databases, password-protected websites, and dynamic content generated on-demand. Think of it as the unseen part of an iceberg.
- Dark Web: A subset of the deep web, the dark web consists of websites and content deliberately hidden from traditional search engines. Accessing it requires specialized software like the Tor browser, which anonymizes web traffic.
Real-Life Example: Your bank account information, accessible only after logging in, resides on the deep web. A forum requiring a specific membership and password to enter would be part of the dark web.
2. Unveiling the Technology: How the Dark Web Works
The dark web operates on a foundation of anonymity and privacy:
- Tor Network: The Tor network is the most commonly used tool for accessing the dark web. It utilizes a series of volunteer-run servers that encrypt and redirect traffic, making it virtually impossible to trace a user’s origin or destination.
- Darknet Markets: These online marketplaces operate on the dark web, facilitating the anonymous buying and selling of a variety of goods and services, both legal and illegal. Transactions often involve cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin for added anonymity.
- Hidden Wiki Links: Websites like “The Hidden Wiki” act as directories, providing links to various dark web sites categorized by content. However, the information listed can be outdated or unreliable, so user caution is advised.
Real-Life Example: Edward Snowden, the NSA whistleblower, used the Tor network to communicate with journalists anonymously while exposing government surveillance programs.
3. A Spectrum of Content: Beyond the Stereotypes
The dark web is not a monolithic entity. It contains a spectrum of content, ranging from the illegal to the surprisingly legitimate:
- Illegal Activities: Drug trafficking, stolen data sales, and illegal weapons marketplaces are some of the dark web’s notorious aspects. Law enforcement agencies constantly work to shut down these illicit operations.
- Real-Life Example: In 2013, the FBI shut down Silk Road, a notorious dark web marketplace known for selling illegal drugs and other contraband.
- Whistleblowing and Censorship Circumvention: Activists and journalists in oppressive regimes can utilize the dark web to communicate securely and bypass government censorship.
- Real-Life Example: During the Arab Spring uprisings, activists in the Middle East used the dark web to organize protests and share information that their governments tried to suppress.
- Privacy-Focused Communication: Some individuals use the dark web for anonymous communication, seeking privacy beyond the reach of government surveillance or corporate data collection.
- Real-Life Example: Journalists communicating with confidential sources or individuals in sensitive professions might utilize the dark web to protect their identities.
4. Navigating the Shadows: Potential Risks and Dangers
The dark web is not without its dangers. Here’s what to be aware of:
- Scams and Fraud: Just like the regular internet, the dark web is susceptible to scams and fraudulent activity. Be wary of deals that seem too good to be true, and never share personal information on any dark web platform.
- Malware and Security Threats: Many dark web sites are poorly secured and can contain malicious software designed to steal data or infect your device. Exercise extreme caution when downloading anything from the dark web.
- Illegal Activity: Even accessing the dark web can raise legal concerns, depending on your location and intent. It’s essential to understand the laws in your region before venturing into this realm.
Real-Life Example: In 2017, a ransomware attack known as WannaCry spread through the dark web, infecting hundreds of thousands of computers worldwide and causing significant financial damage.
5. A Balancing Act: Law Enforcement and the Dark Web
Law enforcement agencies face a continuous challenge in monitoring and policing the dark web:
- Encryption and Anonymity: The very technologies that provide anonymity for legitimate uses also make it difficult for law enforcement to track illegal activity on the dark web.
- Global Reach: The decentralized nature of the dark web
The Dark Web: Exploring the Hidden Layers of the Internet (~300 whistleblowers)
The internet, as most of us know it, is a vast ocean of information readily accessible through search engines like Google or Bing. But beneath the surface lies a hidden realm known as the dark web. This shrouded corner of the internet, often conjuring images of illegal activity and criminal marketplaces, is a complex and misunderstood concept. This comprehensive exploration delves into the dark web, examining its origins, the technology that facilitates it, its potential dangers, and its surprising legitimate uses.
1. Demystifying the Deep Web vs. Dark Web
It’s crucial to distinguish between the deep web and the dark web:
- Deep Web: This encompasses all content not indexed by search engines. It includes private databases, password-protected websites, and dynamic content generated on-demand. Think of it as the unseen part of an iceberg.
- Dark Web: A subset of the deep web, the dark web consists of websites and content deliberately hidden from traditional search engines. Accessing it requires specialized software like the Tor browser, which anonymizes web traffic.
Real-Life Example: Your bank account information, accessible only after logging in, resides on the deep web. A forum requiring a specific membership and password to enter would be part of the dark web.
2. Unveiling the Technology: How the Dark Web Works
The dark web operates on a foundation of anonymity and privacy:
- Tor Network: The Tor network is the most commonly used tool for accessing the dark web. It utilizes a series of volunteer-run servers that encrypt and redirect traffic, making it virtually impossible to trace a user’s origin or destination.
- Darknet Markets: These online marketplaces operate on the dark web, facilitating the anonymous buying and selling of a variety of goods and services, both legal and illegal. Transactions often involve cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin for added anonymity.
- Hidden Wiki Links: Websites like “The Hidden Wiki” act as directories, providing links to various dark web sites categorized by content. However, the information listed can be outdated or unreliable, so user caution is advised.
Real-Life Example: Edward Snowden, the NSA whistleblower, used the Tor network to communicate with journalists anonymously while exposing government surveillance programs.
3. A Spectrum of Content: Beyond the Stereotypes
The dark web is not a monolithic entity. It contains a spectrum of content, ranging from the illegal to the surprisingly legitimate:
- Illegal Activities: Drug trafficking, stolen data sales, and illegal weapons marketplaces are some of the dark web’s notorious aspects. Law enforcement agencies constantly work to shut down these illicit operations.
- Real-Life Example: In 2013, the FBI shut down Silk Road, a notorious dark web marketplace known for selling illegal drugs and other contraband.
- Whistleblowing and Censorship Circumvention: Activists and journalists in oppressive regimes can utilize the dark web to communicate securely and bypass government censorship.
- Real-Life Example: During the Arab Spring uprisings, activists in the Middle East used the dark web to organize protests and share information that their governments tried to suppress.
- Privacy-Focused Communication: Some individuals use the dark web for anonymous communication, seeking privacy beyond the reach of government surveillance or corporate data collection.
- Real-Life Example: Journalists communicating with confidential sources or individuals in sensitive professions might utilize the dark web to protect their identities.
4. Navigating the Shadows: Potential Risks and Dangers
The dark web is not without its dangers. Here’s what to be aware of:
- Scams and Fraud: Just like the regular internet, the dark web is susceptible to scams and fraudulent activity. Be wary of deals that seem too good to be true, and never share personal information on any dark web platform.
- Malware and Security Threats: Many dark web sites are poorly secured and can contain malicious software designed to steal data or infect your device. Exercise extreme caution when downloading anything from the dark web.
- Illegal Activity: Even accessing the dark web can raise legal concerns, depending on your location and intent. It’s essential to understand the laws in your region before venturing into this realm.
Real-Life Example: In 2017, a ransomware attack known as WannaCry spread through the dark web, infecting hundreds of thousands of computers worldwide and causing significant financial damage.
5. A Balancing Act: Law Enforcement and the Dark Web
Law enforcement agencies face a continuous challenge in monitoring and policing the dark web:
- Encryption and Anonymity: The very technologies that provide anonymity for legitimate uses also make it difficult for law enforcement to track illegal activity on the dark web.
- Global Reach: The decentralized nature of the dark web, with servers spread across the globe, makes international cooperation crucial for effective enforcement efforts.
- Real-Life Example: Europol, the European Union’s law enforcement agency, collaborates with international partners to combat cybercrime on the dark web, including shutting down illegal marketplaces and apprehending criminals.
6. Mitigating Risks and Responsible Exploration
If you’re considering venturing into the dark web, here are some crucial steps to minimize risks:
- Understanding the Law: Research the laws in your region regarding accessing and using the dark web. Certain activities might be legal elsewhere but carry legal consequences in your jurisdiction.
- Prioritize Security: Use a reputable antivirus and anti-malware software with real-time protection. Consider using a virtual private network (VPN) for additional anonymity. Never use your personal computer or email address for dark web activities.
- Be Cautious with Downloads: Refrain from downloading anything from the dark web unless you are absolutely certain of its source and legitimacy. Utilize a dedicated computer for dark web exploration if necessary.
- Beware of Scams: If something seems too good to be true on the dark web, it most likely is. Be wary of unsolicited offers or deals that promise easy money or illegal goods.
- Maintain Anonymity: Avoid sharing any personal information on the dark web, including your name, location, or email address. Use strong, unique passwords for any accounts you create.
7. Beyond the Headlines: Legitimate Uses of the Dark Web
While the dark web’s association with illegal activity is prevalent, there are legitimate uses for this hidden corner of the internet:
- Protecting Privacy: Individuals in professions concerned about data privacy, like journalists or whistleblowers, can utilize the dark web for anonymous communication and information sharing.
- Censorship Circumvention: Activists and citizens in countries with strict internet censorship can access information and communicate freely through the dark web.
- Secure Communication: Some individuals and organizations prioritize extreme privacy and utilize the dark web for secure communication beyond the reach of traditional surveillance methods.
- Journalistic Investigations: Investigative journalists might leverage the dark web to contact confidential sources or access information not readily available on the surface web.
- Freelance Marketplaces: A small number of legitimate freelance marketplaces operate on the dark web, catering to individuals seeking anonymity for their work or clients.
Real-Life Example: WikiLeaks, a controversial organization known for publishing classified information, utilizes the dark web for secure communication and document sharing.
8. The Future of the Dark Web: A Continuous Evolution
The dark web is constantly evolving, with law enforcement agencies and developers continuously adapting their strategies:
- Law Enforcement Advancements: Law enforcement agencies are developing new technologies and techniques to track activities on the dark web, making it more challenging for criminals to operate with impunity.
- Decentralized Technologies: The rise of blockchain technology and decentralized applications could potentially create new dark web environments that are even more resistant to traditional censorship and surveillance methods.
- Focus on Privacy: The growing public awareness of online privacy concerns could lead to increased legitimate use of the dark web by individuals seeking greater control over their data.
9. Conclusion: The Dark Web – A Complex Landscape
The dark web is a multifaceted phenomenon, encompassing both illegal activities and legitimate uses. Here are some key takeaways:
- The Dark Web is Not Inherently Evil: While the dark web harbors illegal activity, it also offers tools for privacy, censorship circumvention, and secure communication for legitimate purposes.
- Understanding the Risks is Crucial: Before venturing into the dark web, it’s essential to be aware of the potential dangers and take necessary precautions to protect your security and privacy.
- Law Enforcement Plays a Role: Law enforcement agencies are constantly working to combat illegal activities on the dark web, making it a dynamic battleground between anonymity and accountability.
- The Future is Uncertain: The constant evolution of technology and the growing public discourse surrounding privacy will likely shape the future landscape of the dark web.
10. Call to Action: Navigate with Caution and Awareness
The dark web exists whether we acknowledge it or not. By understanding its purpose, the technologies that facilitate it, and the potential dangers, we can engage in informed discussions about its impact on society. If you choose to explore the dark web, do so with caution, prioritize security, and prioritize responsible usage that respects the law and protects your privacy. The dark web can be a powerful tool, but like any tool, it’s crucial to understand its potential risks and wield it responsibly.
